The forest sector is one of the most important cornerstones of the Latvian economy. To increase green wealth, more than 40 thousand ha of forest are restored every year, about half of which is planted or sown. Researchers from Riga Technical University (RTU) and partners are developing an automated solution for controlling young forest maintenance to help young forests grow stronger and of higher quality.
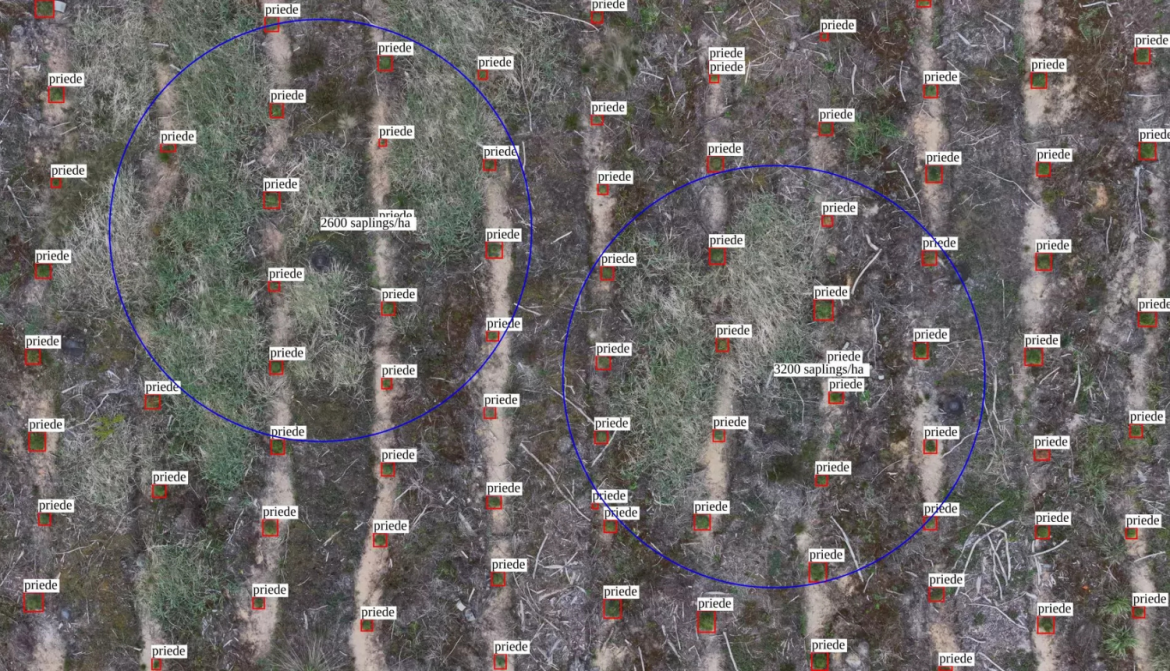
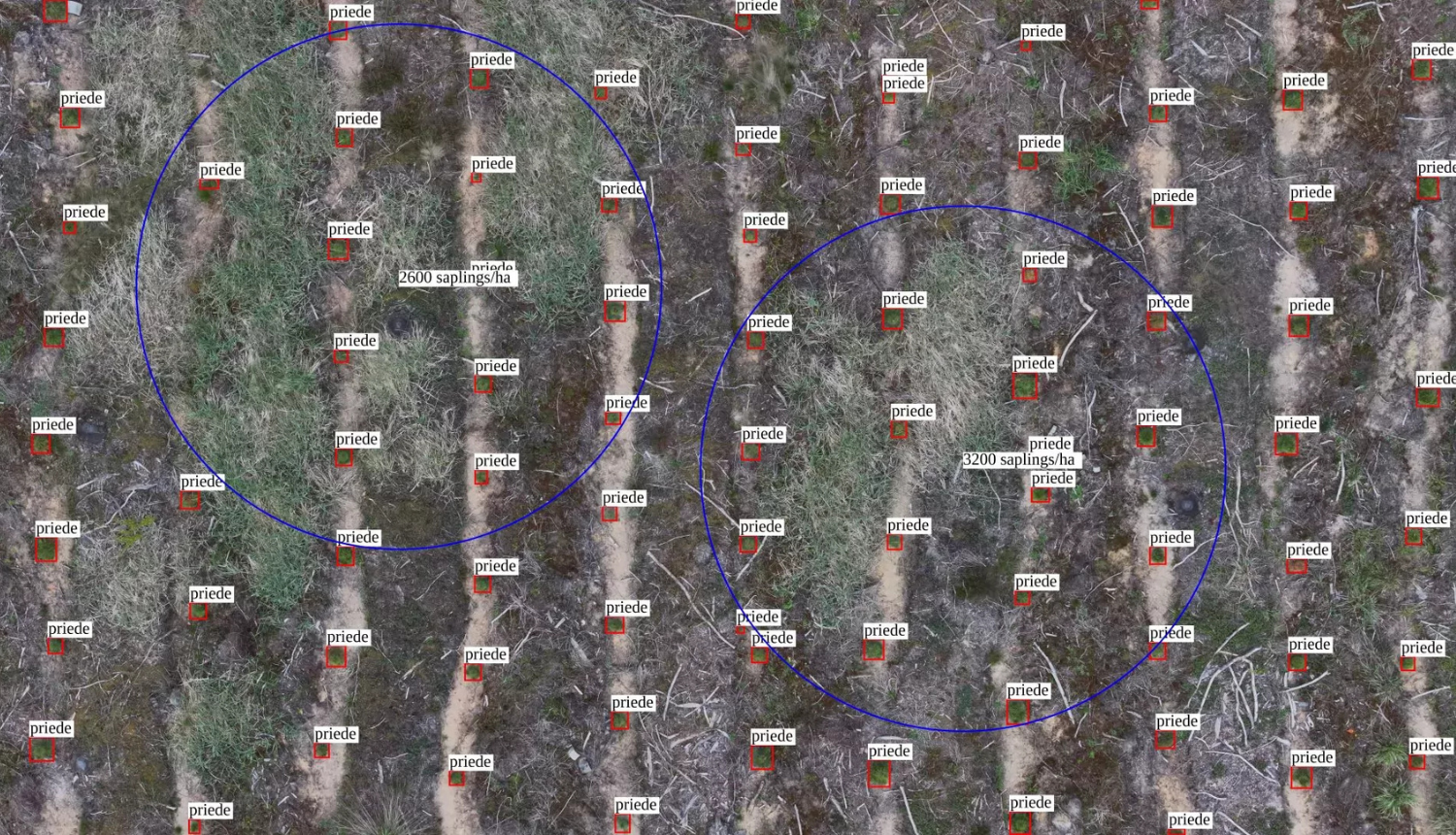
Young pine and spruce stands are surveyed with a drone, and the data obtained is automatically loaded into an application that, using artificial intelligence and computer vision methods, provides forest owners with immediate and objective information about the condition and development of a specific forest area. Such a solution is being demonstrated to the industry by a team of researchers from the Institute of Applied Computer Systems of the Faculty of Computer Science, Information Technology and Energy of RTU.
"In the first two or three years after planting a forest, agrotechnical care must be carried out to reduce overgrowth, which negatively affects the growth of young trees and promotes diseases. It is also necessary to determine promptly whether the seedlings have died out so that they can be restored and, if necessary, management can be adjusted. Care of young stands enhances the health of trees and their annual wood growth. In the long term, the amount of renewable resources also increases, biodiversity is preserved, and climate change is reduced, as forest stands bind more CO2," explains Andrejs Zujevs, a leading researcher at the Institute of Applied Computer Systems, scientific leader of the project "Automated unmanned aerial vehicle system for the control of young stand care."
RTU implemented the project in cooperation with SIA "Rīgas meži", Latvian State Forestry Institute "Silava", Forestry Services Cooperative Society "Mežsaimnieks", SIA "Sodra Forest Latvia" and SIA "MANS MEŽS". Agrotechnical care and its control are carried out manually; however, as the areas of young stands increase, the lack of human resources can negatively impact the quality of care. To create an automated solution that works with high accuracy, researchers inspected young stands with an uncrewed aerial vehicle (various commercially available drones were tested) and mapped the data, prepared a machine learning library, developed, tested and validated software for assessing agrotechnical care work, determining tree density and dead trees in young stands. The dataset used for training the neural network consisted of over 570,000 images.
"Preparing a qualitative data set is one of the main prerequisites for artificial intelligence tools to subsequently work correctly," reminds A. Zujevs.
Initially, the researchers planned to teach the solution to assess not only young pine and spruce trees but also young stands of several deciduous trees, including birches. However, it was found that it is difficult to detect small birches in images taken by the drone using computer vision - their foliage blends in with the background. Larger deciduous trees were detected with the help of computer vision, but it was almost impossible to see trees one to three years old. In turn, testing and validation of the solution in real conditions - in young stands - confirmed that detecting coniferous trees does not pose any challenges. To achieve the best possible results, the researchers have also prepared guidelines for piloting drones, including optimal weather conditions, times of day, speed, height, and image capture modes. There is currently no automated solution available on the European market for controlling the agrotechnical care of young stands. Therefore, the researchers aim to continue improving the innovation and are evaluating the possibility of commercialising it and creating a start-up. They are also interested in developing robotic sapling care equipment that, in the future, would be able to automatically determine the location of saplings in saplings and mow the vegetation around them. By reducing the amount of manual labour, the forestry sector would become increasingly efficient.