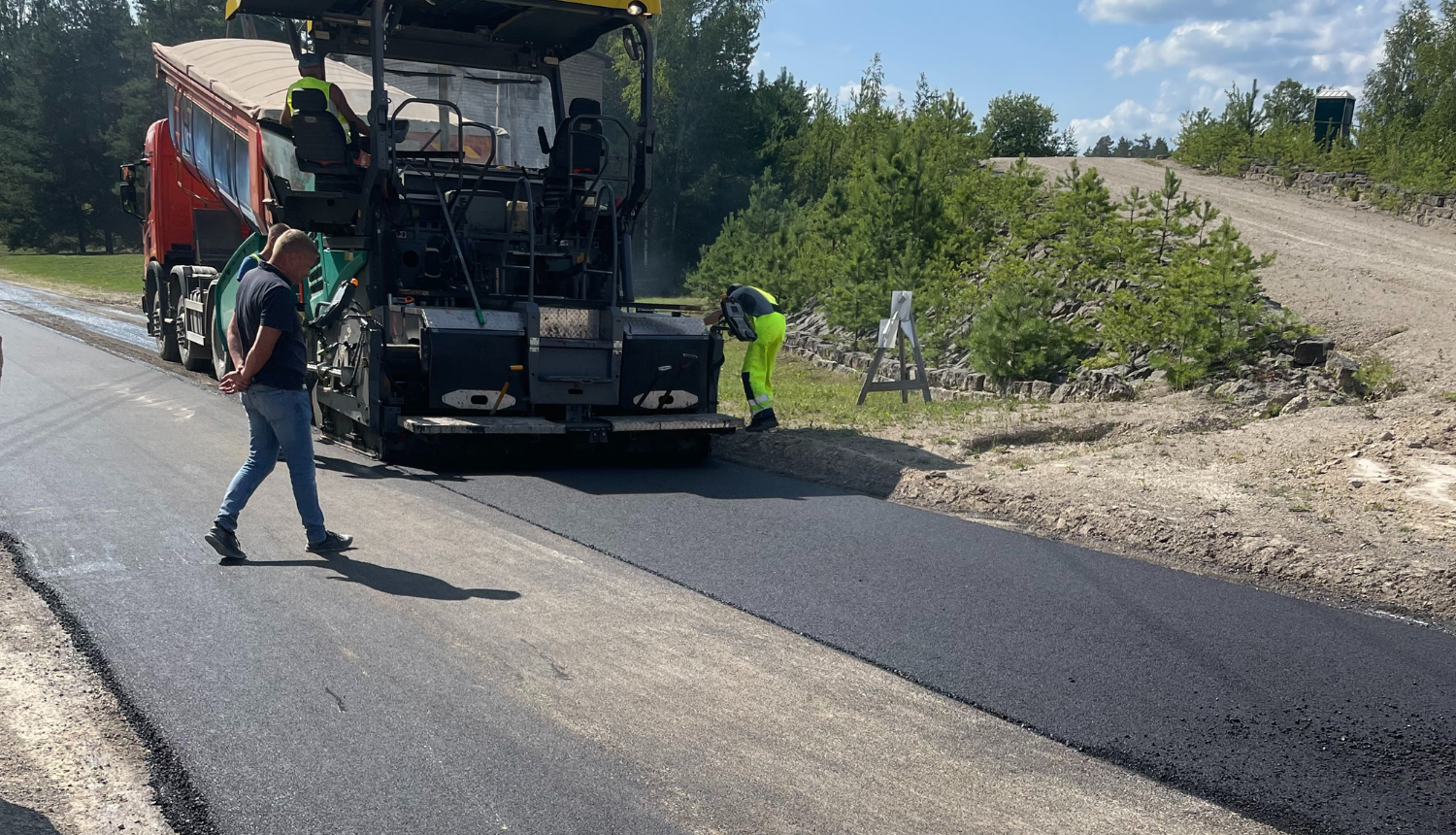
Scientists from the Riga Technical University (RTU) have developed an innovative method for modifying bitumen and asphalt concrete with recycled tire rubber, making road surfaces two to three times more resistant to ruts and cracks while contributing to sustainability in road construction. This technology has been successfully tested not only in Latvia but also, for the first time, in the United States. RTU's laboratories are also creating "recipes" for roads in other countries.
The first experimental road section in the U.S. was constructed in Kansas City, using an asphalt concrete modifier and technology previously tested in Latvia.

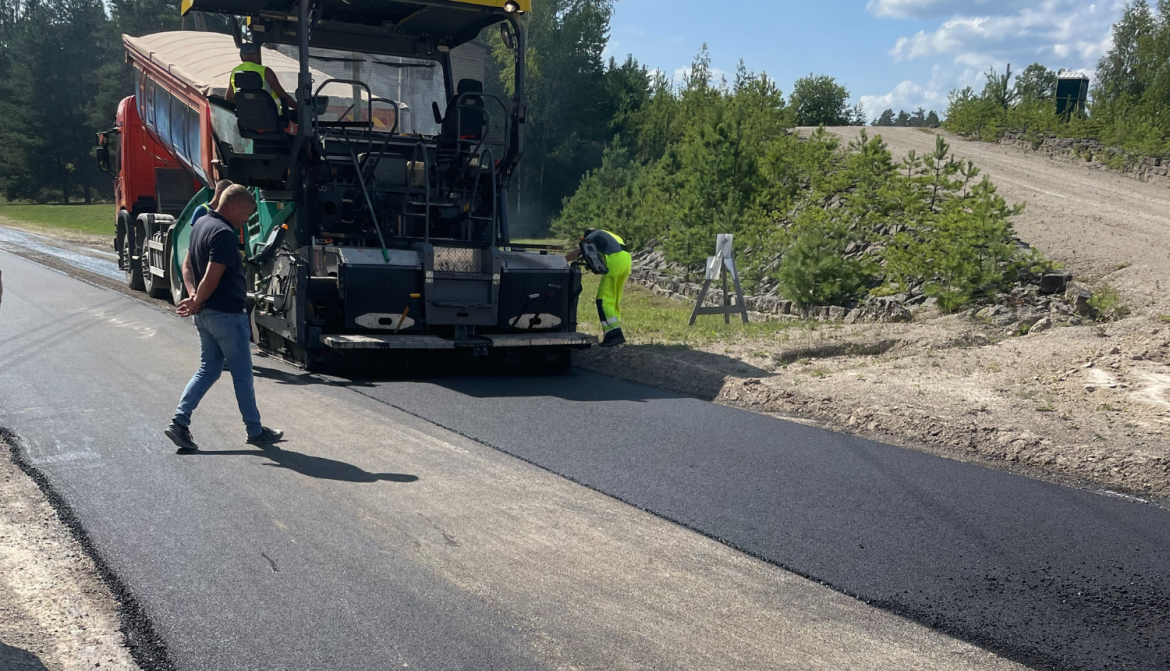
Last year, an experimental batch of asphalt concrete was produced and laid near a large dolomite quarry in Viļāni municipality, in collaboration with SIA "Vlakon". This road segment, heavily used by trucks, became the third "tire asphalt" road in Latvia.
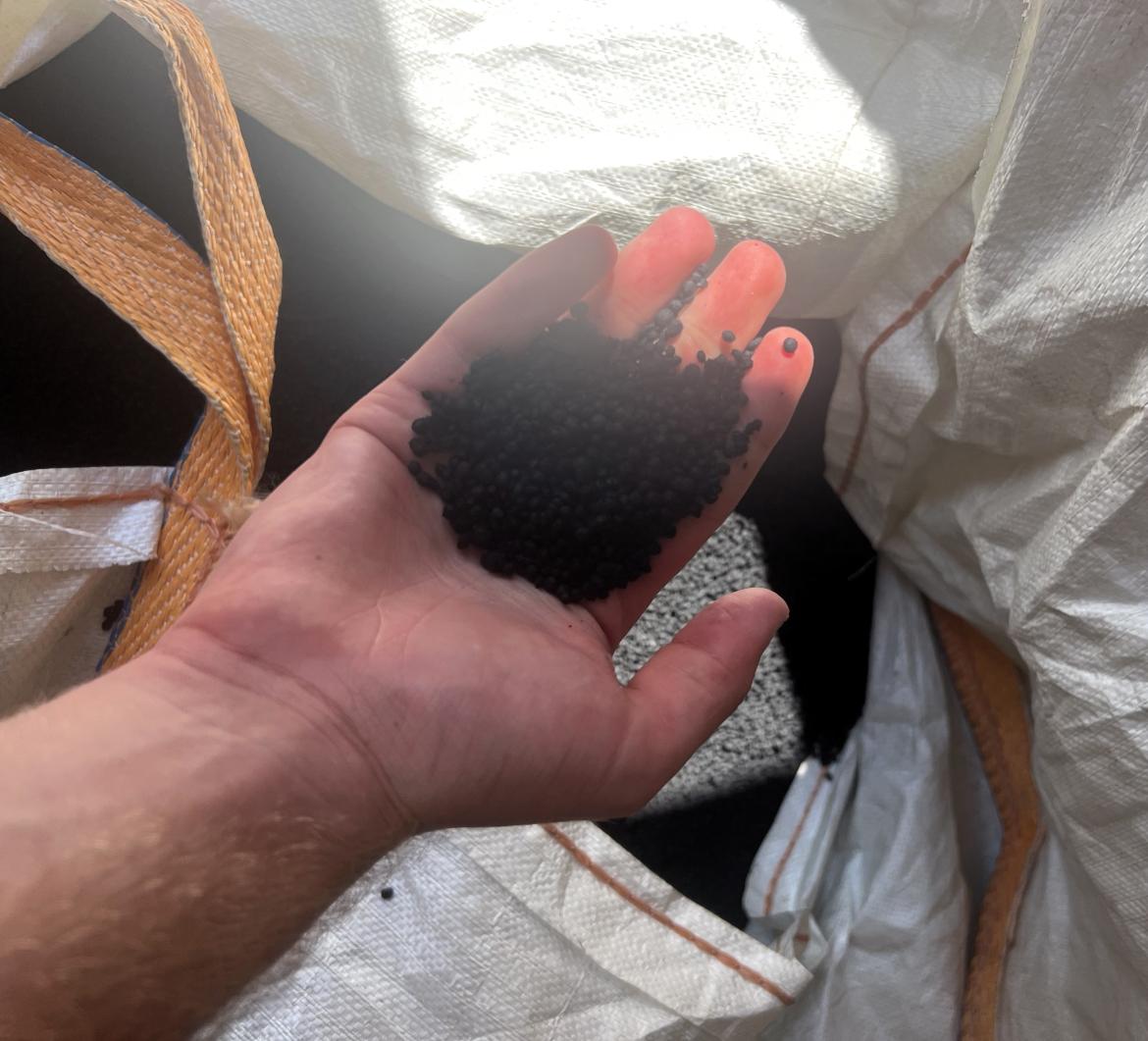
The ELTC (End of Life Tire Compound) modifier used in both the U.S. and Latvia is made from devulcanized recycled tire rubber. RTU scientists collaborated with the U.S. company “Rubbintec” and the Lithuanian company “Polylema” to develop the product. The modifier is added directly to the asphalt concrete mix using the so-called dry method. This new modification technology enhances the properties of road surfaces within a very short production time-up to one minute.
"The technology is simple to implement and does not require significant investments, as there is no need to create a separate modification unit. This makes it applicable in any asphalt concrete production facility. Previously, we used the wet method, where bitumen was modified in a separate unit and then added to the mineral materials during asphalt production. This process took one to two hours. The new technology can be compared to adding sugar to tea - it dissolves immediately, significantly reducing energy consumption," explains Viktors Haritonovs, a leading researcher at the RTU Faculty of Civil Engineering and Mechanical Engineering

RTU's team of scientists from the Institute of Civil Engineering and the Institute of Chemistry and Chemical Technology at the Faculty of Science and Technology continues to develop "recipes" that meet the road construction requirements of Israel, South Korea, Australia, and Germany.
“We have extensive experience and methods for creating and characterizing modified bitumen compositions. We develop and test hundreds of bitumen recipes, evaluating material properties such as rheology - viscosity, plasticity, elasticity, etc. We test the integration of modifiers, simulate their behavior during production, and analyze their performance during use,” says Professor Remo Merijs-Meri from the Institute of Chemistry and Chemical Technology. RTU’s scientific equipment allows, for example, the simulation of seven to ten years of road aging within 24 hours.
RTU scientists' efforts promote the principles of a circular economy and sustainability in road construction.
“It is crucial for us that, as green components become mandatory in road construction procurements, industry companies remain competitive,” says Viktors Haritonovs.
The innovative technology already competes with fossil-based polymers and will become even more advantageous when procurement processes require proof not only of the operational properties of materials but also their minimal environmental impact.

RTU publicity images are available online.