The activities of the Latvian State Institute of Wood Chemistry (LSIWC)between 2019 and 2025 demonstrate how scientific innovation is transformed into new materials, industrial products, and even technologies for space missions. This visual and analytical report highlights the institute’s role in advancing a sustainable bioeconomy by analysing research trends, funding structures, and industry collaboration.
Research Focus and Development Dynamics (2019–2025)
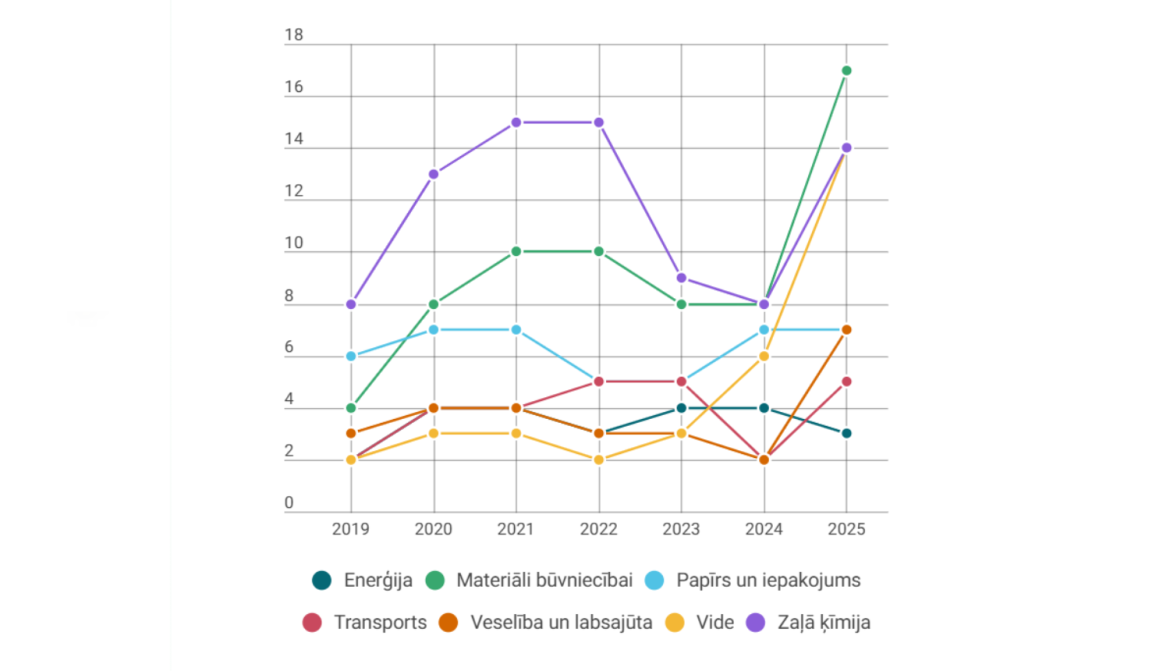
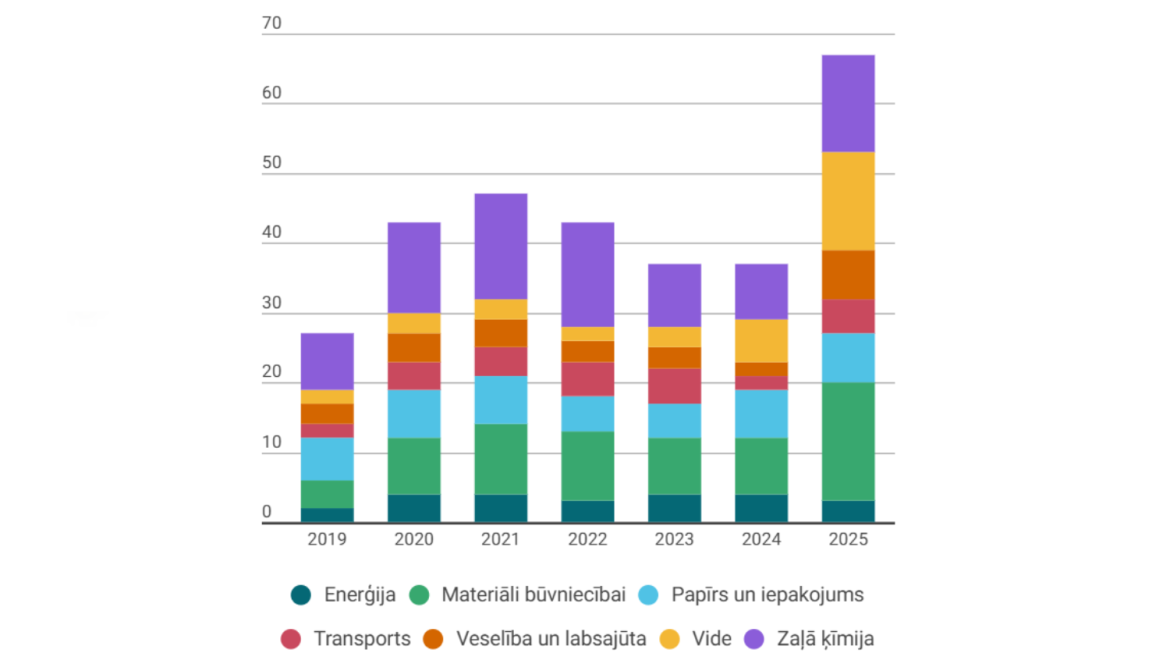
From 2019 to 2025, LSIWC has demonstrated strategic consistency and a clear thematic focus, particularly in the field of green chemistry, with 8 to 15 projects implemented annually. This sustained activity reflects the institute’s leadership in developing biodegradable and renewable raw materials and circular economy solutions. Notably, research in construction materials has increased significantly, reaching 17 projects in 2025, indicating the institute’s ability to respond to the global demand for environmentally friendly, bio-based solutions. The institute’s research covers a wide range of applications — from thermal insulation and wood protection to composite materials and plant protection. International cooperation with more than 20 countries and participation in European research programmes remain vital pillars of the institute’s development.
Funding and Industry Collaboration (2019–2025)
LSIWC’s funding portfolio from 2019 to 2025 demonstrates a balanced development between national, European, and industry sources. The majority of funding comes from EU programmes and international funds, including Horizon Europe — totalling nearly €10 million, with over €4.5 million in 2025 alone. The Latvian Council of Science has also provided stable support for fundamental research and early-career researchers.
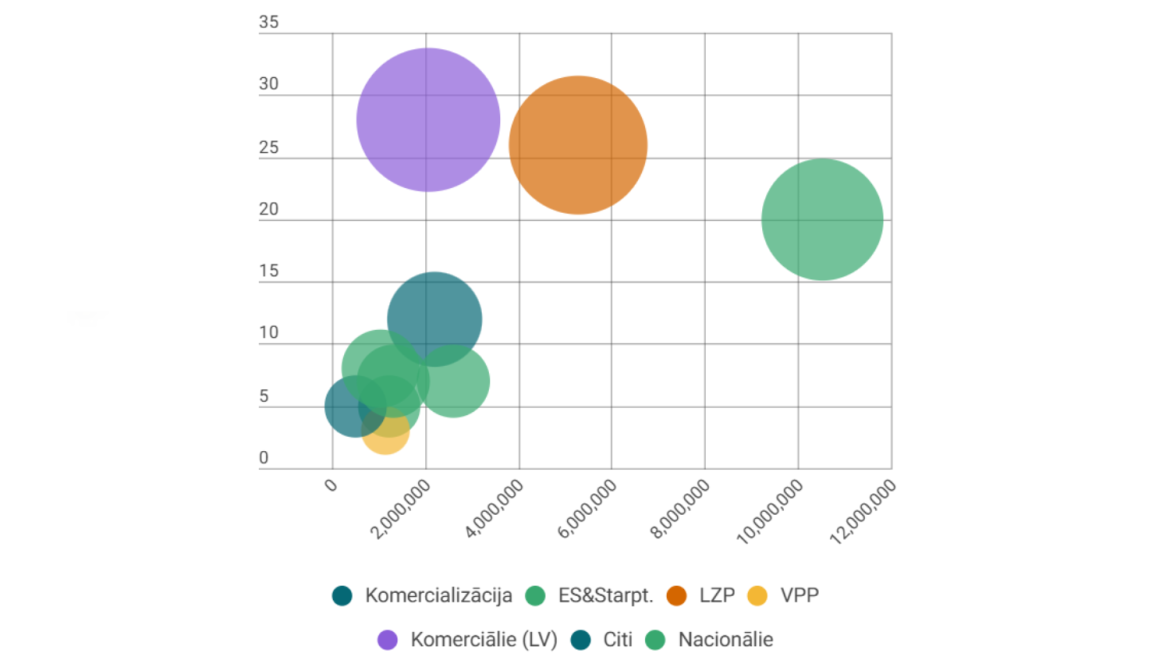
The institute ensured economic impact by implementing over 100 joint projects with partners, developing high-value biomass-based products, and encouraging R&D investments through both external funding and direct cooperation with national and international stakeholders. Companies use this knowledge to strengthen their competitiveness in the growing bio-based materials and product markets.
Based on LSIWC technologies, the leading Baltic plywood producer Latvijas Finieris established the birch bark extraction pilot plant Betulin Lab in 2022. LSIWC has also commercialised several products, creating brands such as SuberBinder, Furfural for Future, RignoCell, and Sustainable Polyols. From 2019 to 2024, industry collaboration — including scientific services, joint research, and technology upscaling — reached €5 million, confirming the institute’s ability to deliver both fundamental and applied economic value.
In 2025, collaboration with Latvijas Finieris expanded with the launch of the first lignin-based resin plant in the Baltics (Viobond project), using technologies developed by LSIWC. This project highlights the institute’s capacity to commercialise research and contribute to market transformation.
Thematic Diversification and Global Achievements (2025)
Although 2025 is not yet complete, data already shows higher thematic diversity and project intensity than in previous years. In addition to traditional fields like green chemistry and construction materials, there has been a notable rise in research activity in environmental topics, packaging, health and well-being, and transportation. LSIWC’s research focus has diversified while maintaining quality and the ability to attract both public and private funding.
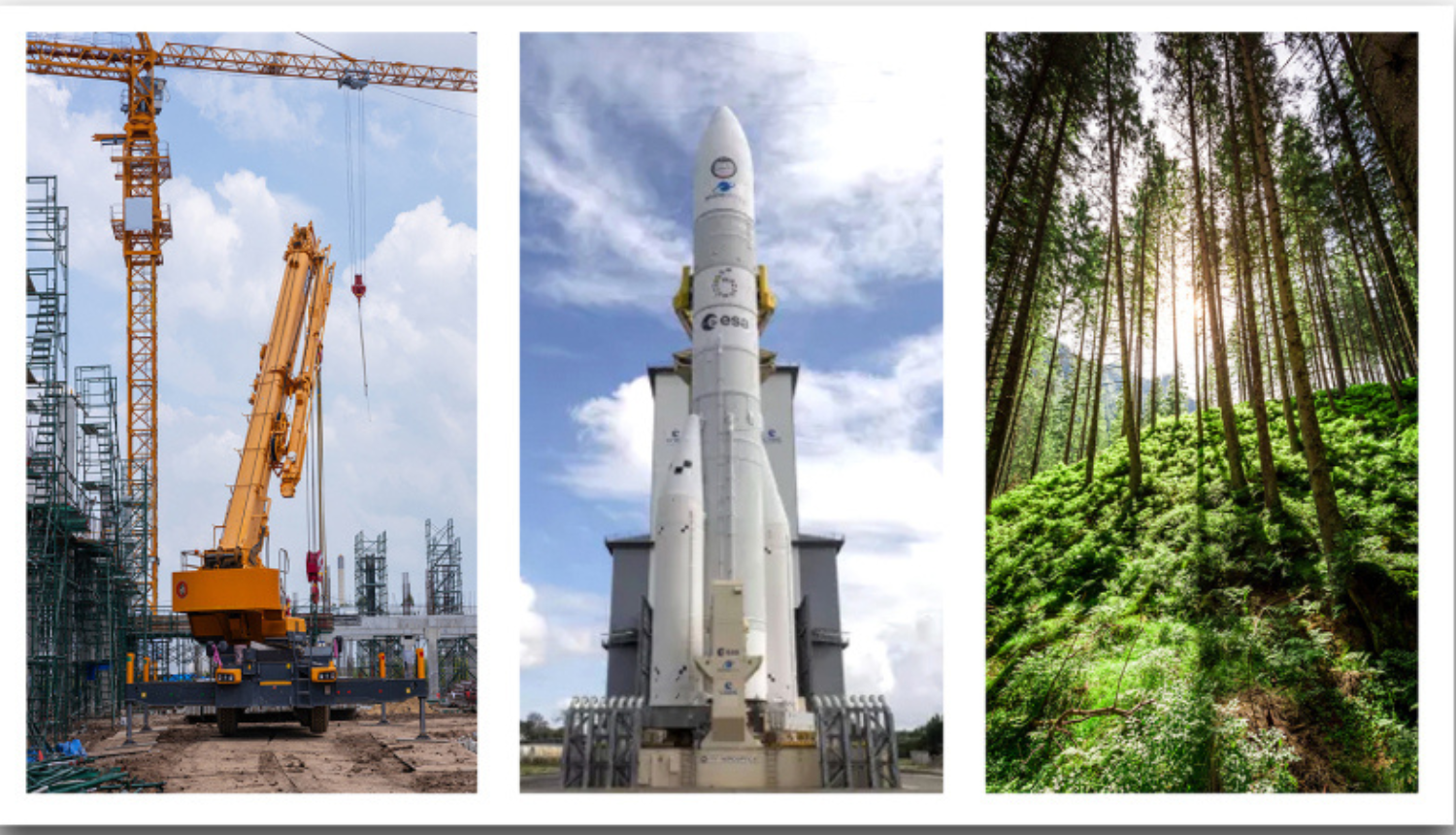
LSIWC’s impact extends far beyond the lab — the institute’s cryogenic polyurethane insulation, capable of withstanding temperatures down to -253 °C, was used in the Ariane-6 launch vehicle’s maiden flight in 2024. This material was developed, tested, and validated at all technology readiness levels (TRL 3–9) and was recognised by the Latvian Academy of Sciences as one of the most significant scientific achievements of 2024. In the same year, construction began on a full-scale lignin-based resin plant in Bolderāja, further confirming LSIWC’s capacity to deliver market-ready technologies based on sustainable raw materials. Overall, the data reveal the institute’s ability to develop diverse bioeconomy directions while simultaneously strengthening expertise in areas essential for achieving sustainability goals. LSIWC has established itself as a globally competitive centre of excellence in bioeconomy, bridging science, industry, and societal needs.


